A clear guide for parents in the UK One of the most common questions parents ask is: When should my child first see a dentist? The simple answer in the UK is: Children should see a dentist by their first birthday, or within six months of their first tooth appearing — whichever comes first. Why…
And are paediatric dentists more expensive? When it comes to children’s dental care, many parents are unsure what is covered by the NHS, whether they need to pay privately, and whether a paediatric (children’s) dentist costs more than a general dentist. The answer depends on where you live in the UK, the type of treatment…

Many people are surprised to learn that dental care can be free during pregnancy in the UK. This support is designed to help protect both your oral health and your baby’s wellbeing at an important time. Are dental treatments free during pregnancy? Yes. If you are pregnant, you are entitled to free NHS dental treatment…

Many patients ask whether dental treatment in the UK is free. The short answer is: most dental care is not free, even under the NHS. Understanding how dental charges work can help you decide the best option for your oral health. Is dental treatment free on the NHS? NHS dental care is not completely free…
Many people wonder how often they really need to visit the dentist. The best check-up schedule depends on your oral health and your risk of dental problems. Regular visits help detect issues early and keep your teeth and gums healthy. The typical recommendation For most patients, a dental check-up every 6 months is a good…

Patients with dental anxiety often ask: can a dentist prescribe diazepam? In the UK, the answer is yes—but only in specific circumstances and under strict rules. What is diazepam? Diazepam is a benzodiazepine medicine that can reduce anxiety, relax muscles, and cause drowsiness. In dentistry, it is sometimes used to help very anxious patients feel…
Patients often ask: can a dentist give a sick note in the UK? The answer is yes—but only in certain situations, and there are limits on what a dentist can and cannot provide. What is a “sick note” in the UK? In the UK, a “sick note” usually means a Statement of Fitness for Work,…
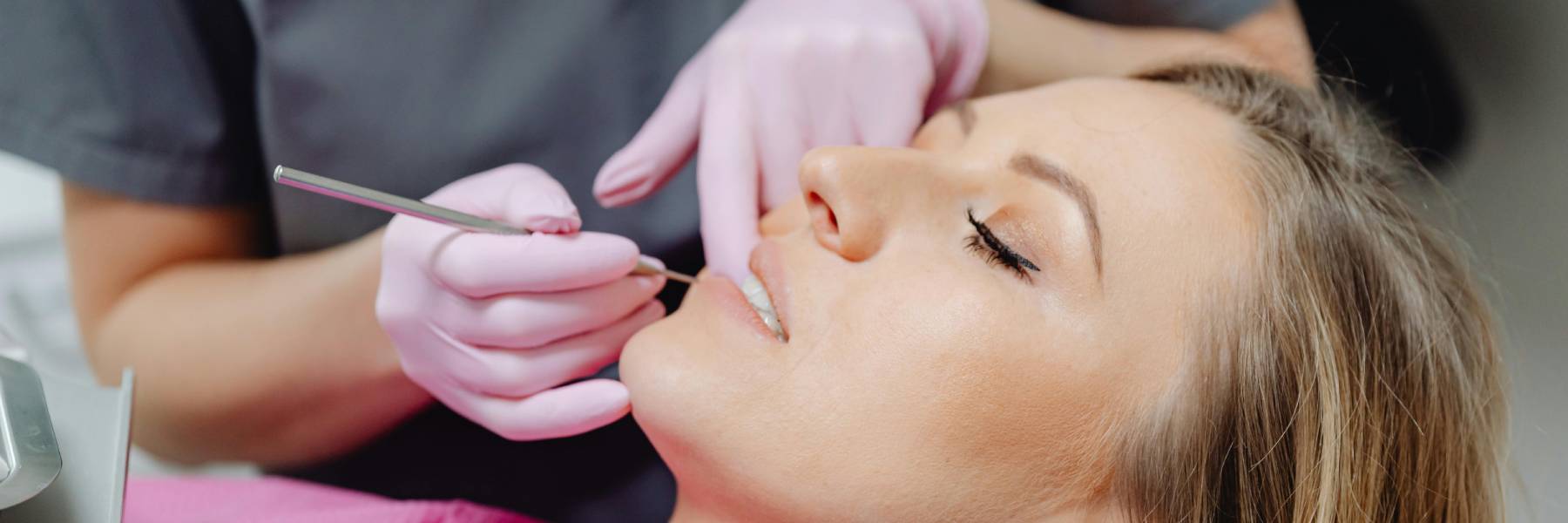
Can a Dentist Put You to Sleep? Many people feel nervous about dental treatment and ask: can a dentist put you to sleep? The answer is yes—but it depends on what you mean by “sleep”, the type of treatment, and whether sedation is suitable for you. Dentists can use different levels of sedation to help…
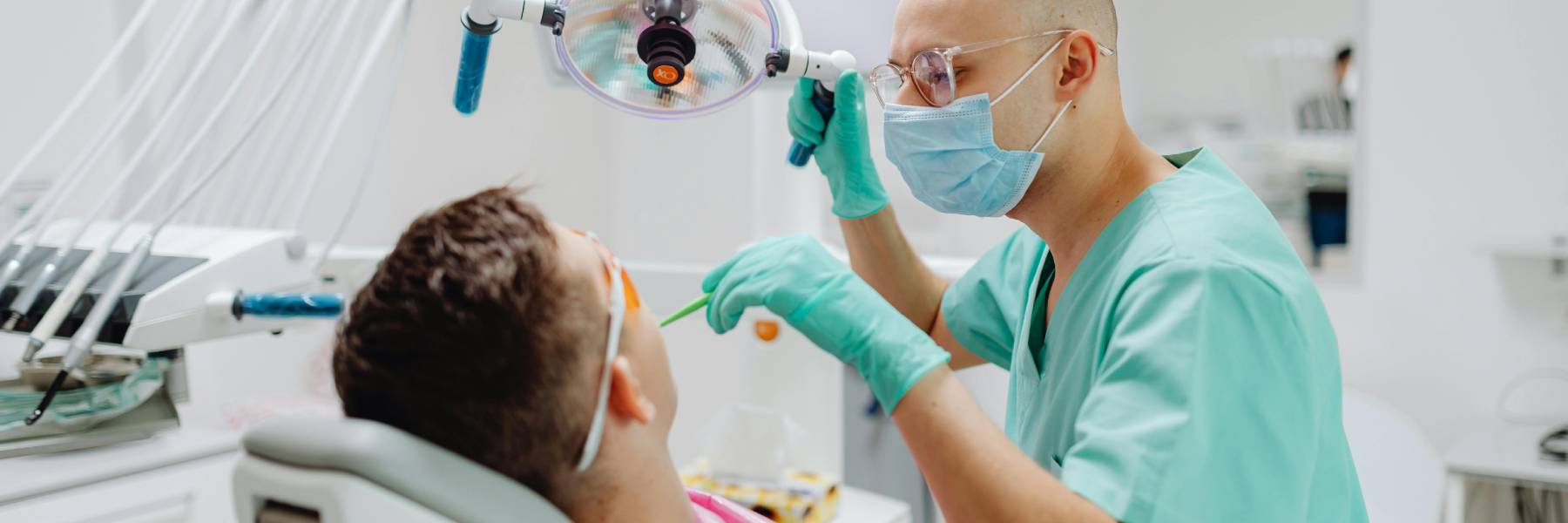
Are Dentists Open on Saturdays? Many people ask this when trying to fit dental care around work, school, or a busy weekday schedule: are dentists open on Saturdays? The answer is yes—some dentists are, but opening hours and availability vary between practices. Are dentists usually open on Saturdays? Not all dental practices open on Saturdays,…

Many patients wonder before a dental appointment: can a dentist tell if you vape? The short answer is yes—often they can, even if you don’t mention it. Vaping can cause noticeable changes to your gums, teeth, saliva, and soft tissues that dentists are trained to spot. How Can a Dentist Tell If You Vape? Dentists…
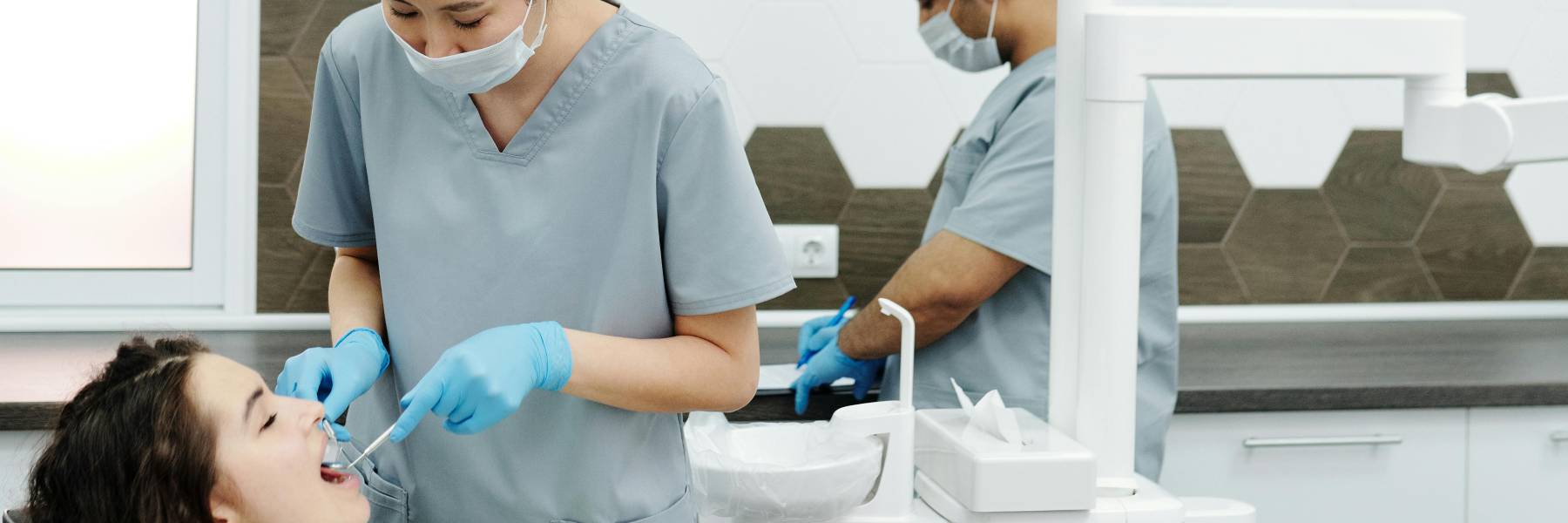
If you’re booking a dentist check-up in London, cost is often the first thing people want to understand. Prices can vary significantly depending on whether you choose NHS or private dentistry, where the practice is located, and what the appointment includes. This guide explains typical London prices and why many patients choose a private check-up—especially…

Teeth whitening is one of the most common cosmetic dental treatments, and it is generally considered safe when it is done properly. But “safe” does not mean “risk-free.” Whitening can cause side effects, and in some situations it can contribute to real damage. The key is understanding what whitening can and cannot do, what the…
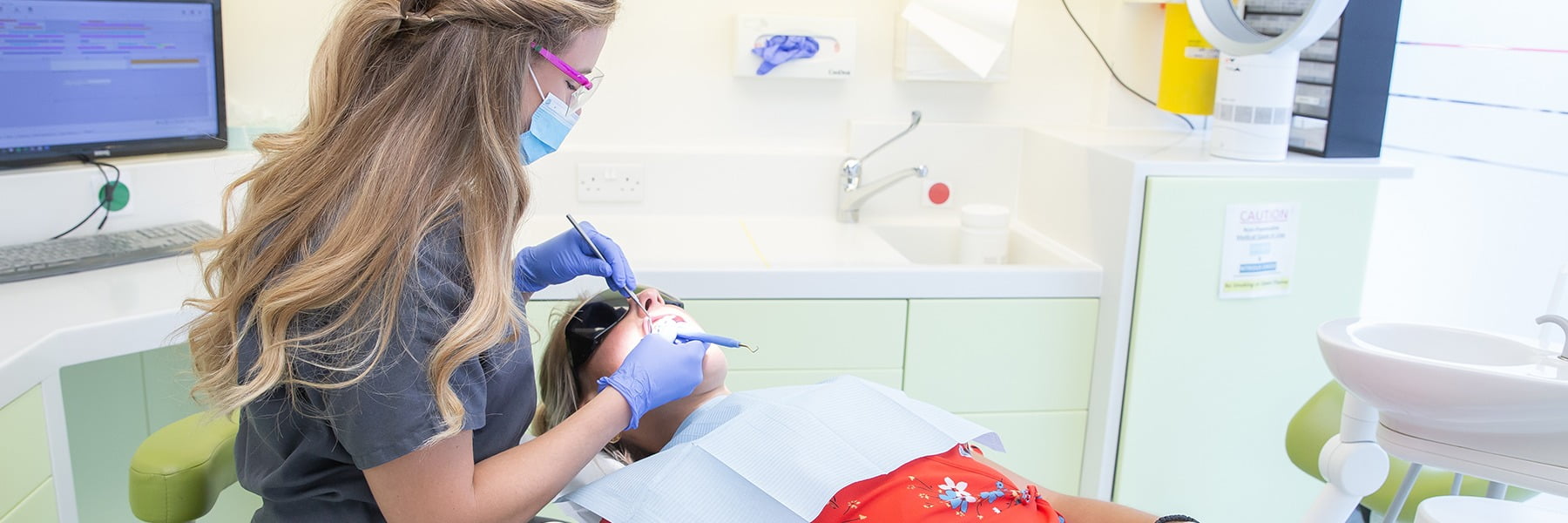
Tooth sensitivity is the most common side effect of teeth whitening. Many people notice short, sharp sensations during or after treatment, especially when eating or drinking something cold. While this can be uncomfortable, it is usually temporary and manageable. This article explains why sensitivity happens during whitening, how long it should last, and what you…

Teeth whitening is designed to lighten the colour of natural teeth, but it does not remove all stains in the same way. Whether whitening works depends on the type of stain, how deep it is, and the overall health of your teeth. This article explains which stains respond well to whitening, which do not, and…

Teeth whitening at the dentist is a popular cosmetic treatment for patients who want a brighter smile in a safe and controlled way. The cost of professional whitening depends on the type of treatment, how quickly results are achieved, and whether whitening is done at home, in the practice, or as a combination of both….

Teeth whitening strips can be safe for many adults when they are used exactly as instructed and the teeth and gums are healthy. Most problems happen when people use strips too often, leave them on too long, or buy unknown “strong” products online. This article explains what whitening strips do, the most common side effects,…

How Long Does Temporomandibular Disorder (TMD) Last? Temporomandibular disorder (TMD) affects the jaw joint (TMJ) and the muscles around it. It can cause pain, clicking, stiffness, headaches and difficulty opening the mouth. One of the most common questions patients ask is: “How long will this last?” The honest answer is: it depends. For many people,…

Night Guards: How They Protect Your Teeth and Relieve Dental Problems Teeth grinding and jaw clenching are very common — especially at night, when you may not realise it’s happening. Over time, this can lead to worn teeth, headaches, jaw pain and broken dental work. At Glow Dental, we often recommend a custom-made night guard…















